Microorganisms like bacteria reproduce by growing and dividing into two new bacteria. The older the bacteria, the more defects they have accumulated. When bacteria divide, the two new bacteria look the same, but the question is whether the defects are divided equally between the two new individuals.
«We wanted to investigate whether the bacteria divided symmetrically with an equal number of defects in both new individuals or whether divided asymmetrically with more defects in one new bacteria than the other," explains Ala Trusina, an associate professor in Biocomplexity at the Niels Bohr Institute at the University of Copenhagen.
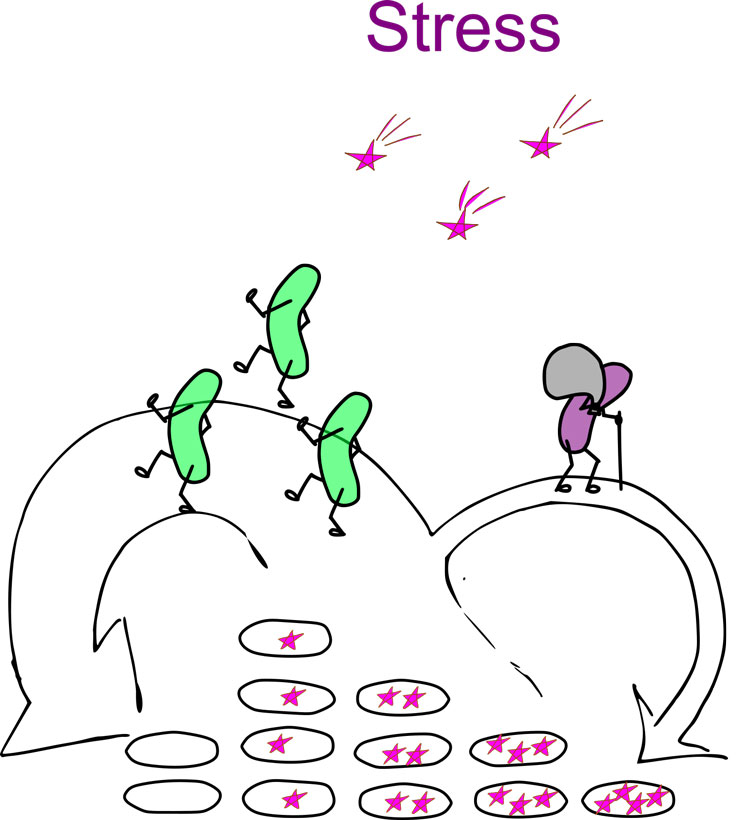
The drawing shows a population where the damage is distributed asymmetrically, so the damage (stars) is constantly being reassigned to a few ‘old’ and slow-growing cells. This means that the population can stay young with no damage and grow faster and produce more healthy offspring. (Credit: Ala Trusina)
The environment controls the colony
In the laboratory they studied the bacterial colonies under different conditions and influences. The measurements showed that when a colony was left in peace, the bacteria shared almost symmetrically, so the new individuals were fairly similar with the same number of defects.
However, if they exposed the colony to ‘stress’ in the form of heat or bacteriostatic compounds, cell division was asymmetrical. Now the defects gathered in one bacterium, which then aged and also grew at a slower rate.
«What we have found is that the asymmetry of cell division is not controlled genetically. It is a process that is controlled by the physical environment. Through collective behaviour, the bacterial colony that is exposed to stress can stay young, produce more offspring and keep the colony healthier. This is completely new knowledge that has never been observed before," explains Ala Trusina.
She explains that the knowledge could have great potential, as it is a process that is probably universal and applies to cells in many organisms, including for stem cells. A single individual cell cannot overcome the damage, but the group of cells can do so together. The strength lies in the collective behaviour.
Source: http://www.nbi.ku.dk/english/news/news16/bacteria-avoid-age-defects-through-collective-behaviour/


