Physical inactivity can result in a weakening of the muscles (known as sarcopenia) and bones (known as osteoporosis). Exercise dispels these frailty, increasing muscle strength and promoting bone formation while suppressing bone resorption. However, exercise therapy cannot be applied to all the clinical cases. Drug therapy may be helpful in treating sarcopenia and osteoporosis, especially when the patients have cerebrovascular disease, dementia or when they have already become bedridden. However, there is no single drug that addresses both tissues simultaneously.
In a new study published in Bone Research, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) developed a novel drug screening system to identify a compound that mimicks the changes in muscle and bone that occur as a result of exercise. Using the screening system, the researchers identified the aminoindazole derivative locamidazole (LAMZ). LAMZ was capable of stimulating the growth of muscle cells and bone-forming cells, osteoblasts, while suppressing the growth of bone-resorbing cells, osteoclasts.
When LAMZ was administrated to mice orally, it was successfully transmitted into the blood, without no obvious side effects. “We were pleased to find that LAMZ-treated mice exhibited larger muscle fiber width, greater maximal muscle strength, a higher rate of bone formation, and lower bone resorption activity,” says lead author of the study Takehito Ono.
The research team further addressed the mode of function of LAMZ and found that LAMZ mimics calcium and PGC-1α signaling pathways. These pathways are activated during exercise and stimulate expression of downstream molecules that are involved in the maintenance of muscle and bone.
The TMDU-led team asked if LAMZ can treat locomotor frailty, LAMZ was administrated to an animal model that has sarcopenia and osteoporosis. “Both oral and subcutaneous administration of drug improved the muscle and bone of mice with locomotor frailty,” says senior author Tomoki Nakashima.
Taken together, the research team’s findings show that LAMZ represents a potential therapeutic method for the treatment of locomotor frailty by mimicking exercise.
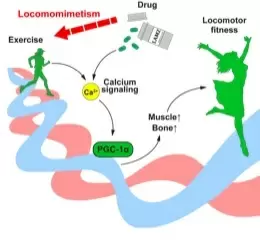
LAMZ augments muscle and bone by mimicking calcium signaling to induce PGC-1α
Exercise induces calcium signaling in the muscle and bone. Under this signaling, PGC-1α is activated, resulting in the augmentation of these tissues. LAMZ, a newly identified locomomimetic drug was found to facilitate the calcium signaling pathway and restores locomotor fitness.
Press Release
tmd.ac.jp


